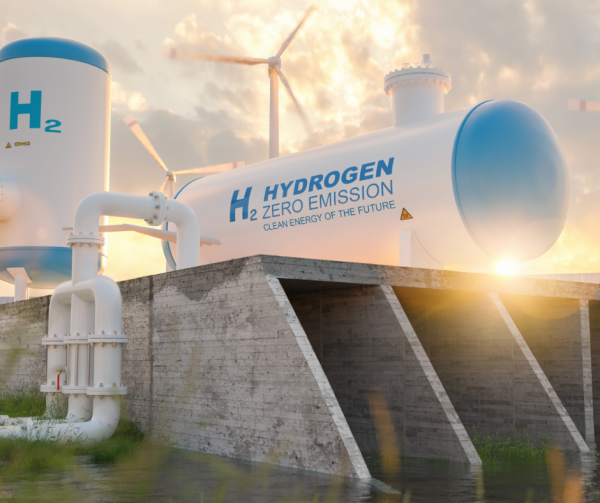
Hydrogen has emerged as a promising clean fuel option in the quest for sustainable energy solutions. Its potential lies in its ability to produce energy without emitting greenhouse gases, offering a pathway towards decarbonization. One of the key advantages of hydrogen is its versatility; it can be produced from various sources, including renewable sources such as wind and solar power, as well as from fossil fuels with carbon capture and storage (CCS) technology. This versatility makes hydrogen a flexible option for addressing different energy needs across sectors such as transportation, industry, and power generation.
However, realizing the full potential of hydrogen as a clean fuel requires overcoming several challenges. One significant challenge is the cost of production. Currently, most hydrogen is produced through steam methane reforming (SMR), a process that relies on natural gas and emits carbon dioxide as a byproduct. Transitioning to low-carbon or carbon-free methods of hydrogen production, such as electrolysis powered by renewable energy, requires significant investment in infrastructure and technological innovation. Additionally, the efficiency of hydrogen production processes needs to be improved to reduce energy consumption and costs further.
Public policy and regulatory frameworks play a crucial role in incentivizing the adoption of hydrogen as a clean fuel. Governments around the world are increasingly recognizing the importance of hydrogen in their energy transition strategies and are implementing policies to support its development and deployment. These policies include financial incentives, research and development funding, regulatory reforms, and collaboration between the public and private sectors. Creating a supportive policy environment can help overcome barriers to the widespread adoption of hydrogen and accelerate its transition to a mainstream energy source.
Challenges in Hydrogen Storage and Transportation

While hydrogen offers promise as a clean fuel, challenges related to storage and transportation must be addressed to unlock its full potential. One significant challenge is the low energy density of hydrogen gas, which makes it challenging to store and transport efficiently. Traditional storage methods, such as compression and liquefaction, require energy-intensive processes and specialized infrastructure. Alternative storage solutions, such as solid-state storage materials and chemical hydrogen carriers, are still in the early stages of development and face technical and economic hurdles.
Another challenge is the development of a comprehensive hydrogen infrastructure for transportation. Unlike conventional fuels, such as gasoline and diesel, hydrogen infrastructure, including production, distribution, and refueling stations, is limited and costly to build. Scaling up hydrogen infrastructure requires significant investment and coordination among stakeholders, including government agencies, energy companies, vehicle manufacturers, and infrastructure developers. Additionally, ensuring the safety and reliability of hydrogen infrastructure is paramount to gaining public acceptance and confidence in hydrogen as a transportation fuel.
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach that involves technological innovation, policy support, and collaboration among stakeholders. Research and development efforts are needed to improve hydrogen storage technologies, develop cost-effective transportation solutions, and enhance the efficiency and reliability of hydrogen infrastructure. Policymakers can play a crucial role in providing financial incentives, regulatory support, and market incentives to spur investment in hydrogen infrastructure and encourage the adoption of hydrogen vehicles. Collaboration among governments, industry players, and research institutions is essential to overcome the technical, economic, and regulatory barriers to the widespread adoption of hydrogen as a clean fuel. At various seminars in Europe that you can visit if you rent a car in Beograd and try to travel comfortably and safely, you can explore all the details of working on such projects from experienced experts in this field.
Integration of Hydrogen in the Energy System
As the world transitions to a low-carbon energy future, the integration of hydrogen into the existing energy system is becoming increasingly important. Hydrogen can play a complementary role to renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power by providing energy storage and grid stability solutions. Hydrogen can be produced during periods of excess renewable energy generation and stored for later use or converted back into electricity through fuel cells or combustion when needed. This can help mitigate the intermittency and variability of renewable energy sources and enhance the reliability and resilience of the electricity grid. Those who have a better understanding of chemistry and physics can quickly understand the possibilities of this subject, however, those for whom it is not their strong point can look for an excellent science tutor in Boulder with whom they will quickly and easily master their material and pass the tests.
In addition to its role in electricity generation, hydrogen can also decarbonize hard-to-abate sectors such as heavy industry and transportation. Industries such as steel, cement, and chemicals rely heavily on fossil fuels for heat and process energy, resulting in significant carbon emissions. By replacing fossil fuels with hydrogen or using hydrogen as a feedstock for low-carbon synthetic fuels and chemicals, these industries can reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to global efforts to combat climate change. The same is true in the auto industry and transportation because the use of hydrogen as a fuel would make a real paradigm shift in cars, and until we get there, you can work on improving your car in the best way possible at a great transmission service in Buffalo.
The integration of hydrogen into the energy system requires careful planning and coordination to maximize its benefits and minimize potential challenges. This includes identifying suitable applications and markets for hydrogen, optimizing the design and operation of hydrogen infrastructure, and ensuring interoperability with existing energy systems. Collaboration among stakeholders, including policymakers, energy companies, utilities, and end-users, is essential to develop cohesive strategies for integrating hydrogen into the energy system and realizing its full potential as a clean, versatile, and sustainable energy carrier. If you run a serious business, you are aware of how important partnerships are in such projects, and if you also need cooperation with reliable companies that will help you succeed, you can look for excellent M&A business advisors who will connect you with the right partners.
Hydrogen Fuel Cells: A Promising Technology
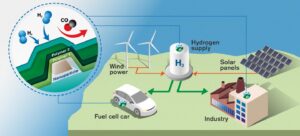
In addition to its role as a clean fuel for transportation and industry, hydrogen fuel cells represent a promising technology for generating electricity with high efficiency and minimal environmental impact. Fuel cells work by converting the chemical energy of hydrogen and oxygen into electricity and heat through an electrochemical reaction. Unlike conventional combustion-based power generation, fuel cells produce electricity without emitting greenhouse gases or other harmful pollutants, making them an attractive option for powering a wide range of applications, from vehicles to stationary power systems. Such systems and factories are of course completely protected by excellent access control systems from Philadelphia that are extremely suitable for installation in private homes or buildings for additional security.
One of the key advantages of hydrogen fuel cells is their high efficiency compared to traditional combustion engines. Fuel cells can achieve efficiencies of up to 60% or higher, significantly higher than internal combustion engines, which typically operate at efficiencies of around 20-30%. This higher efficiency translates into lower fuel consumption and reduced operating costs, making fuel cells an economically viable option for applications where energy efficiency is critical, such as electric vehicles and distributed power generation. This is also another in a series of disadvantages of ordinary motors on classic energy sources that quickly wear out and break down due to constant work and low efficiency, but in order to be less affected if an unexpected car breakdown occurs while you are on a trip, you can rely on to a great roadside assistance app.
Fuel cells also offer several environmental benefits, including reduced greenhouse gas emissions and improved air quality. Because fuel cells produce electricity through an electrochemical reaction, they do not generate any air pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter, or sulfur dioxide (SO2), which are associated with combustion-based power generation. As a result, fuel cell vehicles and stationary power systems have the potential to significantly reduce air pollution and mitigate the adverse health effects associated with traditional fossil fuel combustion. This ecological step would significantly improve the current very bad situation of the air above the planet, which is often full of bad and poisonous gases from factories and cars, states the health clinic in Marietta GA, and if you still feel some of the symptoms or a cough, you can seek the advice of their experienced doctors.
However, despite their potential advantages, hydrogen fuel cells face several challenges that must be addressed to enable their widespread adoption. One of the main challenges is the cost of fuel cell systems, which remains relatively high compared to conventional power generation technologies. The high cost of fuel cells is primarily due to the use of expensive materials such as platinum and other noble metals as catalysts, as well as the complex manufacturing processes involved in producing fuel cell stacks and components. An internet service provider that manages IT services in San Antonio provides its users with excellent internet with which they can explore the details of such projects and express their opinions about these interesting and eco-friendly ideas.
Hydrogen Infrastructure Development
Another critical aspect of realizing the full potential of hydrogen as a clean fuel is the development of a comprehensive hydrogen infrastructure that encompasses production, distribution, and refueling facilities. Unlike conventional fuels such as gasoline and diesel, which have well-established supply chains and infrastructure networks, hydrogen infrastructure is still in the early stages of development and faces several technical, economic, and regulatory challenges. Something that it still has is excellent publicity because a lot of people already know about this kind of project and it helps to realize something like this in the future. If your business needs good publicity, consider contacting an excellent Colorado Springs SEO company that will create a promotion plan for you that will help the general public learn about your brand and ideas faster.
One of the main challenges is the limited availability of hydrogen production facilities and refueling stations, particularly outside of major urban areas. Currently, most hydrogen production facilities are located near industrial centers or in regions with abundant renewable energy resources, such as wind and solar power. Expanding the geographic coverage of hydrogen infrastructure will require significant investment in new production facilities, distribution pipelines, and refueling stations, as well as regulatory reforms to streamline permitting and approvals processes. Significant investments in a secure future are something that concerns you, and if you want to invest wisely in one of the properties suitable for a pleasant life, you can consider the beautiful houses in Boca Falls that are spacious and very affordable.
In addition to expanding the physical infrastructure for hydrogen production and distribution, efforts are also needed to address safety and regulatory concerns related to hydrogen storage and transportation. Hydrogen is highly flammable and can pose safety risks if not handled properly. Ensuring the safe and secure storage, handling, and transportation of hydrogen requires the development and implementation of rigorous safety standards and protocols, as well as training and certification programs for personnel involved in hydrogen operations. While working on such jobs, employees must be provided with adequate equipment, and if you are involved in a sport or physical activity, think about the right combat clothing that will be comfortable for you and will help you feel more comfortable while working towards your goal.
Hydrogen in the Built Environment
Beyond transportation and industry, hydrogen also has the potential to play a significant role in the built environment, including residential, commercial, and institutional buildings. Hydrogen can be used as a clean and efficient energy source for heating, cooling, and powering appliances and equipment, offering an alternative to natural gas and other fossil fuels commonly used in buildings. This could be an environmentally friendly and pleasant way to provide affordable heating for everyone, with which you can easily and quickly heat water for a relaxing bath in your home, but if you aspire to such a pleasant and relaxing ritual, you will also want to visit a luxury spa in Toronto.
One promising application of hydrogen in the built environment is combined heat and power (CHP) systems, also known as cogeneration systems, which simultaneously generate electricity and heat from a single fuel source. Hydrogen-powered CHP systems can provide a reliable and resilient energy supply for buildings, reducing dependence on the grid and enhancing energy security. Additionally, hydrogen can be used in fuel cell-based micro-CHP systems, which are well-suited for residential and small commercial buildings, providing both electricity and heat on-site. In this way, you can relax on cold winter days while enjoying delicious mulled wine from special crystal wine glasses in the comfort and warmth of your home.
In addition to CHP systems, hydrogen can also be used in fuel cells for backup power generation in buildings, providing emergency power during grid outages or other disruptions. Fuel cell backup power systems offer several advantages over traditional diesel generators, including lower emissions, quieter operation, and higher efficiency. These systems can be integrated seamlessly into existing building infrastructure, providing a reliable and environmentally friendly source of backup power. You will be able to relax in a pleasant energy source that is ecological and works to heat the entire building while enjoying your favorite book and delicious milk chocolate edibles.
Hydrogen as a Renewable Energy Carrier

In addition to its role as a clean fuel and energy source, hydrogen also has the potential to serve as a renewable energy carrier, facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power into the energy system. Hydrogen can be produced from water through electrolysis using electricity generated from renewable sources, such as wind turbines and solar panels, effectively storing excess renewable energy in the form of hydrogen for later use. Members of youth organizations such as Readathon school fundraiser are working every day to improve their reading hobbies and improve their abilities to ensure such ecological and convenient systems in the future.
One of the key advantages of hydrogen as a renewable energy carrier is its ability to store and transport energy over long distances and periods, overcoming the intermittency and variability of renewable energy sources. Hydrogen can be stored in large quantities and transported via pipelines, trucks, or ships to locations where it is needed, such as urban centers or industrial facilities. Once delivered, hydrogen can be converted back into electricity through fuel cells or used directly as a fuel for various applications. Such an ecological and safe source of energy for traffic has not existed since horsemen on their faithful horses with traditional saddle blankets, and with this fuel of the future, the ecological condition of the planet will be significantly improved after a long time.
In addition to its role in storing and transporting renewable energy, hydrogen can also enable the production of renewable fuels such as hydrogenated vegetable oil (HVO), synthetic methane, and ammonia, which can be used as drop-in replacements for conventional fossil fuels in existing infrastructure. These renewable fuels offer a low-carbon alternative to conventional fuels and can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions from sectors such as transportation, industry, and agriculture. Rent a car in Beograd and at the attended European seminars on traffic and agriculture you can meet excellent scientists who are actively working on such projects and who will simply explain to you the essence of this large and important project.
The Path Forward for Hydrogen
In conclusion, hydrogen holds tremendous promise as a clean, versatile, and sustainable energy carrier with the potential to transform the way we produce, store, and use energy. From transportation and industry to the built environment and renewable energy integration, hydrogen offers solutions to some of the most pressing challenges facing our global energy system, including climate change, air pollution, and energy security. Get involved in some of the excellent hospitality courses where you will find out all the ways this will affect tourism as well as all the valuable benefits of different tourist destinations and places worth visiting.
However, realizing the full potential of hydrogen will require concerted efforts and investments from governments, industry players, and other stakeholders. This includes supporting research and development initiatives to drive technological innovation, implementing supportive policies and regulatory frameworks to incentivize investment and deployment, and fostering collaboration and partnerships to address technical, economic, and regulatory barriers.
By working together to overcome these challenges and seize the opportunities presented by hydrogen, we can accelerate the transition to a more sustainable, resilient, and prosperous energy future for generations to come. With vision, leadership, and commitment, hydrogen can play a central role in shaping a cleaner, greener, and more sustainable world for all.